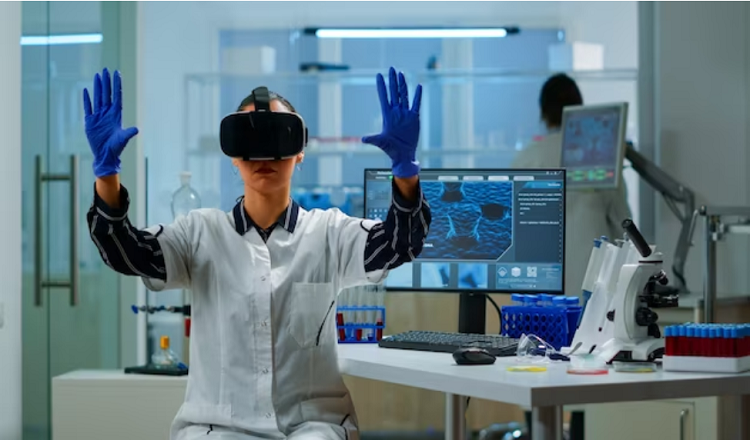
Virtual Reality (VR) has been around for a while now, but its use in healthcare is still in its infancy. With the rapid advancements in technology, VR is quickly becoming one of the most innovative tools in the medical industry. In this blog, we’ll be diving into the world of Virtual Reality in Healthcare and Medicine and exploring the exciting benefits and challenges that come with this cutting-edge technology.
The history of Virtual Reality in Healthcare dates back to the mid-1960s when a MIT researcher named Ivan Sutherland developed the first VR head-mounted display. It has come a long way since then, and today VR technology is being used in a variety of medical applications, from surgical simulations to mental health therapy. With its ability to immerse patients in a virtual environment, VR has the potential to revolutionize the way medical professionals diagnose, treat, and educate their patients. However, as with any new technology, there are also challenges that come with implementing VR in healthcare, and we’ll be exploring those in this article as well.
Virtual Reality in Healthcare
Virtual Reality has brought numerous benefits to the healthcare industry. Here are some of the ways that VR technology is changing the game for patients and medical professionals alike:
- Improved patient outcomes: One of the biggest advantages of VR in healthcare is its ability to improve patient outcomes. By using VR simulations, medical professionals can practice complex procedures, test out new techniques, and refine their skills, all without risking harm to real patients. Additionally, VR can be used to help patients manage chronic pain, improve physical therapy outcomes, and even help treat mental health conditions like anxiety and depression.
- Enhanced medical training and education: VR technology is also changing the way medical professionals receive training and education. With VR simulations, medical students can experience real-life scenarios in a safe and controlled environment, allowing them to develop their skills before working with actual patients. This leads to better prepared and more confident medical professionals, which ultimately benefits patients.
- Reduced cost and increased access to medical care: VR technology can also help to reduce the cost of medical care and increase access to it. For example, VR simulations can be used to train medical professionals in developing countries, where access to expensive equipment or training facilities may be limited. Additionally, VR-based treatments can be delivered remotely, making it easier for patients to receive care from the comfort of their own homes.
- Improved patient experience: VR technology can also enhance the overall patient experience by reducing pain, improving recovery times, and providing a more engaging and interactive experience for patients. For example, VR simulations can be used to distract patients during procedures, reducing the need for anesthesia and minimizing the risk of complications.
- Advancement in medical research: Finally, VR technology is also helping to advance medical research by providing a safe and controlled environment for testing and experimentation. With VR, researchers can simulate real-life scenarios and study the effects of various treatments and procedures, leading to new breakthroughs and innovations in the medical field.
Challenges of Virtual Reality in Healthcare
While Virtual Reality technology has brought numerous benefits to the healthcare industry, there are also some challenges that come with its implementation. Here are some of the obstacles that need to be overcome in order to fully realize the potential of VR in healthcare:
- Technical difficulties and limitations: One of the biggest challenges facing VR in healthcare is the technical difficulties and limitations that come with the technology. VR systems require high-end hardware and software, and can be complex to set up and operate. This can lead to technical difficulties and limitations that can impact the quality of VR-based treatments and limit their accessibility.
- High cost of VR technology: Another challenge is the high cost of VR technology. VR systems can be expensive to purchase, install, and maintain, which can limit their accessibility and impact their adoption in the healthcare industry.
- Lack of standardization and regulation: There is currently a lack of standardization and regulation in the VR healthcare industry, which can lead to confusion and inconsistencies in the quality of VR-based treatments. This can make it difficult for patients to determine which VR systems are safe and effective, and can limit the adoption of VR in the healthcare industry.
- Privacy and security concerns: VR technology also raises privacy and security concerns. With VR-based treatments, personal health information is being stored in digital form, which can be vulnerable to hacking and cyber attacks. This can put patients’ personal information at risk and create security concerns for medical professionals.
- Resistance to change among healthcare professionals: Finally, there may be resistance to change among healthcare professionals. Many medical professionals are used to traditional methods of treatment and may be resistant to adopting new technologies like VR. This can slow down the adoption of VR in the healthcare industry and limit its impact.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Healthcare and Medicine
Here is a list of some of the components in healthcare and medicine where virtual reality (VR) is being used:
- Surgical simulation and training: VR technology is used to provide surgeons with realistic and interactive simulations of complex surgical procedures.
- Pain management and rehabilitation: VR is used to help manage pain and improve physical rehabilitation outcomes.
- Mental health therapy: VR is used to treat various mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
- Medical visualization and diagnosis: VR technology is used to provide medical professionals with enhanced visualization and diagnostic capabilities.
- Patient education and engagement: VR is used to educate and engage patients about their health and medical conditions.
- Clinical trials: VR is used to simulate the effects of drugs and treatments in a controlled environment.
- Physical therapy: VR is used to provide interactive and immersive exercises that can help improve patients’ mobility and functionality.
- Telemedicine: VR is used to provide remote medical consultations and treatments, increasing access to medical care.
- Medical research: VR is used to advance medical research by allowing scientists to study human anatomy, physiology, and pathology in a simulated environment.
- Medical device development: VR is used to design and test new medical devices and equipment, improving the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
These are just a few examples of how VR is being used in healthcare and medicine. As VR technology continues to evolve, it is likely that new applications will emerge, further improving the quality of medical care and patient outcomes.
Conclusion
virtual reality (VR) technology is poised to play a significant role in the future of healthcare and medicine. The potential benefits of VR are vast and include improved patient outcomes, enhanced medical training and education, reduced cost and increased access to medical care, improved patient experience, and advancement in medical research. Despite these potential benefits, there are also challenges associated with the use of VR in healthcare, including technical difficulties and limitations, high cost of VR technology, lack of standardization and regulation, privacy and security concerns, and resistance to change among healthcare professionals.
However, despite these challenges, the future of VR in healthcare and medicine is bright. As VR technology continues to evolve, it will likely be used to improve the quality of medical care and patient outcomes in new and innovative ways. The potential of VR in healthcare is only beginning to be realized, and there is a pressing need for further research and development in this field.